Services
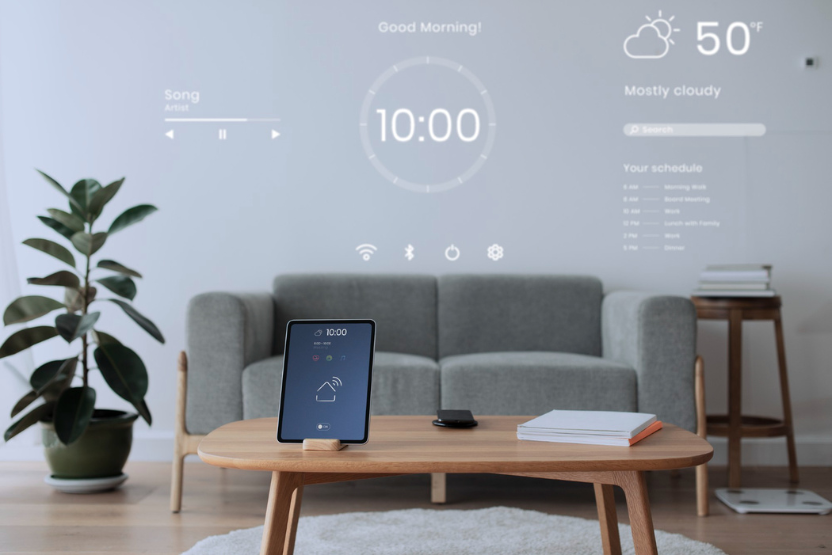
Home Automation
Home automation involves using technology to control and automate various aspects of your home, making it more convenient, energy-efficient, and secure. Here are some examples of home automation:
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Lighting Automation
– Control lights remotely using smartphones or voice assistants
– Schedule lighting scenes for different times of the day
– Adjust brightness and color temperature
Security and Surveillance
– Install security cameras with motion detection and alerts
– Control door locks and gates remotely
– Receive notifications when someone enters or exits your home
Climate Control
– Adjust temperature settings remotely using thermostats
– Schedule temperature changes for different times of the day
– Monitor energy consumption
Entertainment Systems
– Control music, video, and lighting systems with a single interface
– Stream content from various sources to different rooms
– Adjust volume and settings remotely
Smart Home Devices
– Amazon Echo (Alexa)
– Google Home
– Apple HomePod
– Samsung SmartThings
Benefits of Home Automation
– Convenience: control your home from anywhere
– Energy efficiency: optimize energy consumption
– Security: monitor and control your home’s security
– Customization: tailor your home’s settings to your preferences
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.Building Automation
Building automation involves using technology to control and monitor various building systems, increasing efficiency, comfort, and safety. Here are some key aspects of building automation:
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.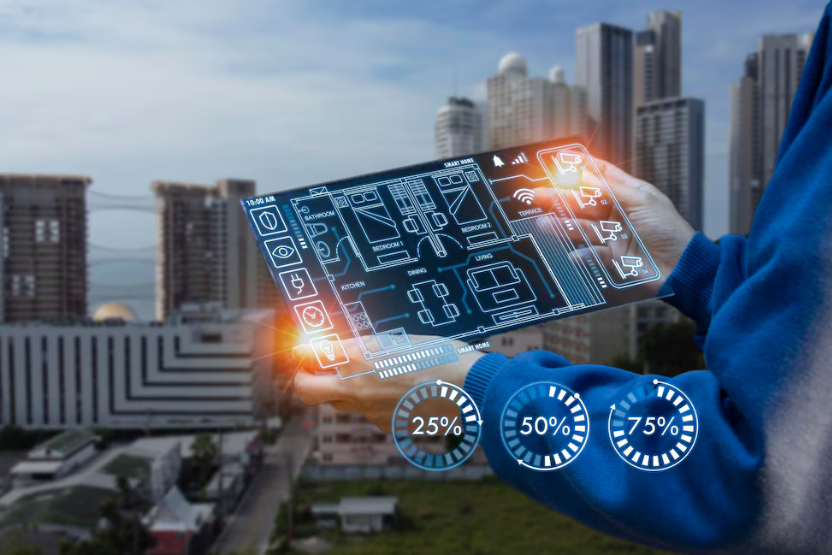
Building Automation Systems (BAS)
1. Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC): Control temperature, humidity, and air quality.
2. Lighting Control: Control lighting levels, scheduling, and energy efficiency.
3. Security and Access Control: Monitor and control access, surveillance, and alarm systems.
4. Fire Safety and Detection: Monitor and control fire detection, suppression, and alarm systems.
5. Elevator Control: Monitor and control elevator operations, safety, and energy efficiency.
Building Automation Technologies
1. Building Management Systems (BMS): Integrate and manage various building systems.
2. Smart Sensors and Devices: Monitor and control building systems, such as temperature, humidity, and lighting.
3. Wireless Communication: Enable wireless communication between devices and systems.
4. Cloud-Based Services: Provide remote access, monitoring, and control of building systems.
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Analyze data, optimize building performance, and predict maintenance needs.
Benefits of Building Automation
1. Energy Efficiency: Optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and lower costs.
2. Increased Comfort: Improve indoor air quality, temperature, and lighting.
3. Enhanced Safety: Monitor and control fire safety, security, and access.
4. Reduced Maintenance: Predictive maintenance, automated scheduling, and reduced downtime.
5. Improved Productivity: Optimize building performance, reduce distractions, and increase occupant satisfaction.
Building Automation Applications
1. Commercial Buildings: Offices, malls, hotels, and hospitals.
2. Industrial Buildings: Factories, warehouses, and manufacturing facilities.
3. Residential Buildings: Apartments, condominiums, and single-family homes.
4. Government Buildings: Offices, courthouses, and public facilities.
5. Educational Institutions: Schools, universities, and research facilities.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.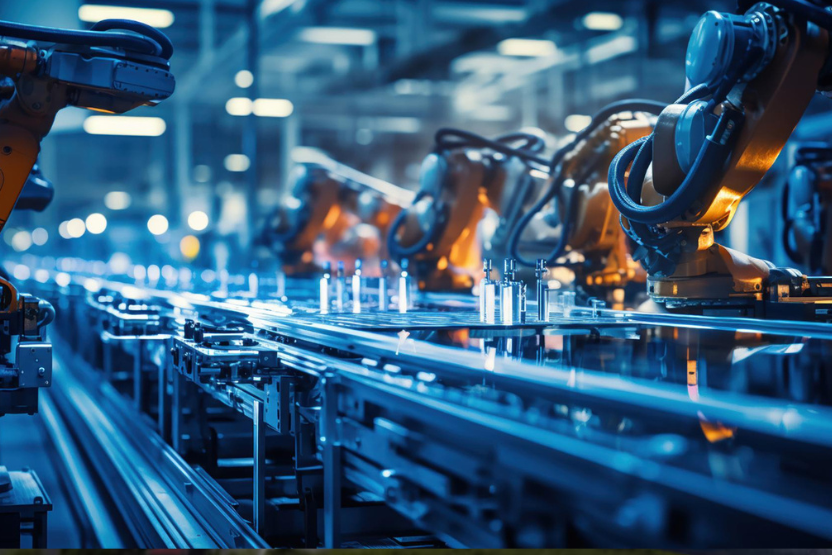
Industry Automation
Industrial automation involves using technology to control and monitor industrial processes, increasing efficiency, productivity, and safety. Here are some key aspects of industrial automation:
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Types of Industrial Automation
1. Process Automation: Control and monitoring of industrial processes, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate.
2. Discrete Automation: Control and monitoring of discrete manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines and robotics.
3. Hybrid Automation: Combination of process and discrete automation.
Industrial Automation Technologies
1. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): Control and monitor industrial processes.
2. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA): Monitor and control industrial processes remotely.
3. Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs): Provide a user interface for operators to interact with industrial processes.
4. Sensors and Actuators: Monitor and control industrial processes.
5. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Connect industrial devices to the internet for remote monitoring and control.
Benefits of Industrial Automation
1. Increased Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks and processes.
2. Improved Productivity: Increase production rates and reduce downtime.
3. Enhanced Safety: Reduce risk of accidents and injuries.
4. Better Quality Control: Monitor and control product quality.
5. Cost Savings: Reduce energy consumption, labor costs, and maintenance costs.
Industries Using Industrial Automation
1. Manufacturing: Automotive, aerospace, chemical, and food processing.
2. Oil and Gas: Refining, drilling, and pipeline management.
3. Power Generation: Fossil fuel, nuclear, and renewable energy.
4. Water and Wastewater: Treatment and distribution.
5. Pharmaceuticals: Production and packaging.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.